In the fast-paced world of financial technology (FinTech), innovation comes with a growing set of risks—from regulatory uncertainty and cybersecurity threats to operational breakdowns and financial volatility. As companies increasingly rely on digital platforms to handle sensitive transactions and customer data, even a single misstep can result in substantial financial losses, reputational damage, or regulatory penalties. That’s where risk management software steps in as a vital shield. Designed to detect, assess, and respond to threats in real time, this software helps FinTech companies stay compliant, secure, and financially stable. By integrating advanced technologies like AI, automation, and predictive analytics, risk management software empowers businesses to not only anticipate potential issues but also take proactive measures to reduce losses and enhance decision-making across the board.
What is Risk Management Software in FinTech?
Risk management software in FinTech is a specialized digital solution designed to identify, assess, monitor, and mitigate various financial and operational risks that digital financial companies face. Unlike traditional risk management methods, this software provides real-time insights, automates compliance checks, and analyzes massive volumes of data to uncover hidden threats. Whether it’s preventing fraud, ensuring regulatory compliance, or managing market and liquidity risks, the software serves as a centralized system that helps FinTech companies make smarter, faster, and more informed decisions. By consolidating risk-related data and streamlining workflows, it enables organizations to build a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to risk—essential in an industry where change happens rapidly and consequences can be costly.
 Types of Risks Faced by FinTech Companies
Types of Risks Faced by FinTech Companies
FinTech companies thrive on innovation, offering faster, smarter, and more accessible financial services. However, with this rapid growth comes a complex web of risks that can undermine stability, customer trust, and long-term profitability. These companies must navigate an environment where digital transactions, regulatory scrutiny, and evolving technologies intersect—often in unpredictable ways. From managing compliance in different jurisdictions to defending against cyberattacks and financial fraud, understanding these risks is the first step toward building a secure and resilient FinTech operation.
Here are the key types of risks FinTech companies commonly face:
1. Regulatory Risks
The FinTech sector operates under strict and constantly changing regulatory frameworks that vary across countries and regions. Regulations such as GDPR, PSD2, AML, and KYC require ongoing compliance. A lack of adherence can lead to hefty penalties, business restrictions, or complete shutdowns—especially for companies operating globally without a centralized compliance strategy.
2. Operational Risks
These risks arise from internal failures such as system outages, process inefficiencies, poor internal controls, or employee errors. In a digital-first industry, even a small operational glitch can lead to transaction errors, data loss, or customer dissatisfaction, ultimately impacting revenue and reputation.
3. Cybersecurity Risks
Handling sensitive financial and personal data makes FinTech companies high-value targets for cybercriminals. Common threats include data breaches, phishing attacks, ransomware, and insider threats. A successful attack can cause significant financial losses, erode customer trust, and trigger regulatory investigations.
4. Financial Risks
This category covers several dimensions:
- Credit Risk: Arises when borrowers fail to repay loans or meet their obligations.
- Market Risk: Fluctuations in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, or asset prices can impact investment portfolios and revenue.
- Liquidity Risk: The inability to meet short-term liabilities due to insufficient cash flow can paralyze operations and damage solvency.
5. Reputational Risks
Trust is a cornerstone of any financial service. Negative press, poor customer experiences, or security lapses can tarnish a FinTech company’s image quickly. In a hyper-connected world, even minor issues can escalate on social media and damage brand credibility overnight.
6. Third-party and Vendor Risks
Many FinTechs outsource core functions—like cloud storage, KYC verification, or payment processing—to external vendors. If these partners experience failures, security breaches, or non-compliance, it directly impacts the FinTech firm. Dependency on a single vendor can also create “vendor lock-in” risks, making it difficult to switch providers without disrupting services.
 Risk Management Strategies in FinTech
Risk Management Strategies in FinTech
As the FinTech industry continues to disrupt traditional financial services with digital innovation, it also faces an ever-expanding array of risks. These can range from cyberattacks and fraud to regulatory violations and market instability. Without a structured approach to risk management, even the most promising FinTech ventures can face significant financial losses, legal consequences, or reputational damage. That’s why developing and implementing well-rounded risk management strategies is crucial—not only to prevent potential threats but also to ensure agility and resilience in a fast-changing environment.
Below are some of the most effective risk management strategies used by FinTech companies today:
1. Risk Avoidance
This is the most straightforward strategy: avoiding activities or operations that carry excessive risk. In practice, this might mean not entering a new market with unstable regulations or opting out of high-risk financial products. For early-stage FinTechs, risk avoidance helps conserve resources and focus on safer, more manageable opportunities.
2. Risk Reduction
Risk can rarely be eliminated, but it can often be minimized. This strategy involves implementing tools, policies, and practices that lower the probability or impact of a threat. Examples include installing advanced firewalls and encryption to combat cyber threats, using machine learning for real-time fraud detection, or segmenting duties internally to reduce human error. Continuous monitoring and regular audits are also part of this approach.
3. Risk Transfer
When FinTech companies cannot fully control a risk, they often transfer it to another party. This is commonly done through insurance—such as cyber liability, errors and omissions (E&O), or regulatory risk coverage. Companies may also outsource certain functions (like cloud storage or payment processing) to experienced third-party vendors with specialized risk controls, though this introduces a new set of risks that also need to be managed.
4. Risk Retention
Not all risks are worth avoiding or transferring. Some are minor, manageable, or unavoidable, and FinTech companies may choose to retain them. This strategy accepts the risk’s presence and prepares for its potential impact, often through contingency planning. For example, a company might accept the occasional chargeback or failed transaction as part of doing business, while ensuring its financial models account for these costs.
5. Diversification
Spreading risk across different products, markets, customer bases, or technologies reduces vulnerability. A FinTech offering both lending and investment products, for instance, can balance losses in one area with gains in another. Geographic diversification—operating in multiple countries—can also reduce the risk associated with local economic downturns or regulatory shifts.
6. Regulatory Compliance Strategy
Navigating the complex and ever-evolving regulatory landscape is a constant challenge. A proactive compliance strategy includes staying updated on legal changes, hiring specialized compliance officers, integrating automation tools to handle reporting and verification (such as KYC/AML processes), and conducting regular internal reviews. This not only prevents fines but also builds credibility with customers and partners.
Key Components of Risk Management Software
Risk management software serves as the backbone of a FinTech company’s defense against financial threats, regulatory penalties, and operational disruptions. It combines technology, analytics, and automation to provide a comprehensive view of risk across the organization. By centralizing data and offering real-time insights, this software empowers decision-makers to act quickly and confidently in an increasingly complex environment. Understanding its key components helps clarify how it works and why it’s essential for modern FinTech operations.
Here are the core components typically found in effective risk management software:
1. Real-Time Risk Monitoring: Enables continuous tracking of transactions, user activity, and system behavior to identify unusual patterns and potential threats as they happen.
2. Data Analysis and Predictive Modeling: Uses historical and real-time data to detect trends, forecast risks, and simulate scenarios, helping businesses anticipate and prevent future issues.
3. Compliance Management Tools: Automates the tracking of regulatory changes and ensures that the company adheres to evolving standards like AML, KYC, and GDPR, reducing the risk of fines or legal trouble.
4. Automated Alerts and Notifications: Provides instant alerts for suspicious activities, compliance breaches, or system errors, allowing for immediate response and mitigation.
5. Integration Capabilities: Seamlessly connects with other systems like CRMs, financial platforms, and customer verification tools to provide a unified risk management approach.
6. Audit Trails and Reporting Dashboards: Tracks all user actions and generates reports for internal audits or regulatory inspections, offering transparency and accountability.
7. User Access Controls and Permissions: Helps limit access to sensitive data and system features based on user roles, reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized activity.
 How Risk Management Software Minimizes Financial Losses
How Risk Management Software Minimizes Financial Losses
In the dynamic and highly regulated world of FinTech, financial losses can stem from a variety of sources—ranging from fraud and system failures to market volatility and non-compliance. These losses aren’t just limited to money; they can damage reputation, disrupt services, and invite legal scrutiny. Risk management software serves as a vital defense system that helps FinTech companies avoid these pitfalls. It brings together real-time monitoring, data analytics, and automation to detect threats early, guide better decision-making, and ensure timely intervention. By turning risk into a manageable and measurable factor, the software allows companies to operate with confidence and stability, ultimately reducing unnecessary financial drain.
Here are key ways risk management software helps minimize financial losses:
1. Early Detection of Fraud and Anomalies
Fraudulent transactions, identity theft, and account takeovers are major threats in FinTech. Risk management software uses real-time data monitoring and behavior analytics to identify patterns that suggest fraud—such as unusual login locations, transaction spikes, or multiple failed logins. By catching these anomalies early, companies can freeze transactions, block accounts, and prevent significant financial damage.
2. Automated Compliance Monitoring
Regulatory violations often result in heavy penalties and operational disruptions. The software keeps track of current and upcoming legal requirements such as AML (Anti-Money Laundering), KYC (Know Your Customer), and GDPR. It automates compliance checks and generates timely reports, helping companies avoid costly fines, investigations, and business restrictions.
3. Improved Credit and Investment Decisions
Poor lending or investment decisions can lead to loan defaults or capital losses. Risk management tools assess customer creditworthiness using predictive models that factor in historical behavior, real-time data, and external credit data. For investment portfolios, the software can simulate market conditions to evaluate risk exposure, helping FinTechs make safer, data-backed financial moves.
4. Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
Manual processes in risk identification and management are prone to delays and errors. Risk management software automates key tasks such as auditing, reporting, and approvals. This reduces human error, shortens response time, and lowers operational costs, allowing companies to reallocate resources to more strategic functions.
5. Real-Time Alerts and Rapid Response
When a risk is identified—whether it’s a policy violation, technical failure, or suspicious activity—the software immediately notifies key personnel. These alerts allow for faster mitigation, such as temporarily disabling access or halting high-risk transactions, preventing small issues from snowballing into expensive problems.
6. Resource Optimization
By providing clear visibility into risk hotspots, the software helps leadership prioritize where to invest time and capital. For instance, it may highlight vulnerabilities in third-party integrations or high-risk customer segments, enabling proactive investments in those areas instead of wasting resources on low-risk zones.
7. Scenario Planning and Stress Testing
Risk management software often includes simulation tools that allow companies to test their responses to various stress scenarios—like a market crash, sudden regulatory change, or mass customer onboarding. This prepares organizations to respond effectively when real-world disruptions occur, minimizing financial impact through advance planning.
How AI Enhances Risk Management in FinTech
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a game-changer in the world of risk management, especially for FinTech companies that deal with vast amounts of data and require quick, accurate decision-making. AI enhances risk management by automating the detection of anomalies, fraud, and suspicious behaviors that may go unnoticed through traditional methods. With the help of machine learning algorithms, AI can analyze historical and real-time data to predict potential risks before they occur, enabling FinTech firms to act preemptively. It also streamlines regulatory compliance by automating KYC and AML checks, reducing the burden on human teams while improving accuracy. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants further aid in handling risk-related queries and customer concerns instantly. Overall, AI not only improves the speed and efficiency of risk identification and response but also ensures smarter, data-driven decisions that minimize financial exposure and boost operational resilience.
Examples of Risk Management Applications in FinTech
Risk management in FinTech is not a one-size-fits-all solution—it involves a range of applications tailored to address specific threats across various business functions. From fraud prevention to compliance automation, FinTech companies leverage technology to stay ahead of potential risks while improving customer trust and operational efficiency. These applications are often powered by AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics, enabling proactive monitoring, real-time alerts, and smarter decision-making. Here are some of the most common and impactful risk management applications in the FinTech space:
1. KYC (Know Your Customer) and Identity Verification: Automated systems verify customer identities using biometric data, facial recognition, and document validation to prevent identity fraud and ensure regulatory compliance.
2. AML (Anti-Money Laundering) Monitoring: Real-time transaction monitoring helps detect and flag suspicious activities like unusually large transfers or frequent international transactions, helping FinTechs meet AML obligations.
3. Transaction Monitoring Systems: These systems continuously scan user activity to identify abnormal behavior, such as duplicate transactions, rapid-fire purchases, or access from unfamiliar IP addresses, which could indicate fraud.
4. AI-Powered Credit Risk Assessment: Machine learning models evaluate a borrower’s creditworthiness using alternative data—like transaction history or social behavior—especially useful for customers without traditional credit scores.
5. Chatbots for Risk Queries and Support: AI-driven chatbots can provide instant responses to customer questions about suspicious account activity, while also guiding users through steps to secure their accounts.
6. Cybersecurity Threat Detection: Advanced software monitors for signs of breaches, malware, phishing attempts, or DDoS attacks, allowing for real-time defense and damage control.
7. Blockchain for Data Integrity and Transparency: Some FinTechs use blockchain to secure transaction records, reduce fraud, and ensure tamper-proof audit trails, especially in cross-border payments and digital asset platforms.
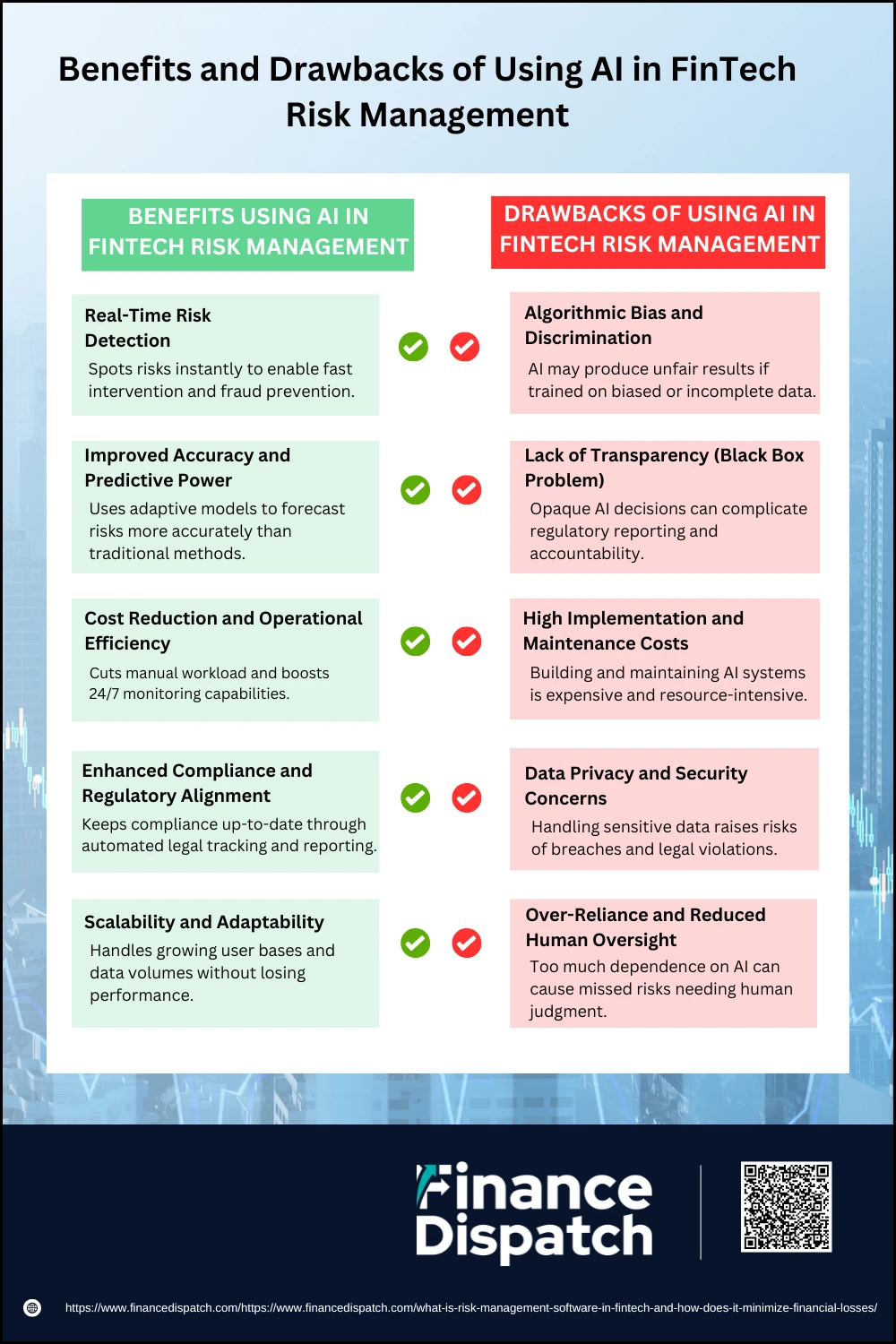 Benefits and Drawbacks of Using AI in FinTech Risk Management
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using AI in FinTech Risk Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly transformed how FinTech companies manage risk by introducing speed, precision, and automation into traditionally manual processes. It allows for real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and enhanced fraud detection, making it a powerful tool in the fight against financial crime and regulatory violations. However, while AI offers many advantages, it also brings challenges such as ethical concerns, potential bias in algorithms, and reliance on large datasets. Understanding both the benefits and drawbacks helps FinTech firms make informed decisions about how to implement AI effectively in their risk management strategies.
Here are the key benefits and drawbacks of using AI in FinTech risk management:
Benefits Using AI in FinTech Risk Management
1. Real-Time Risk Detection
AI systems can analyze thousands of data points in milliseconds to spot suspicious activity as it happens. This immediate response is crucial in preventing fraud, unauthorized transactions, or system breaches before they escalate into serious financial issues.
2. Improved Accuracy and Predictive Power
Traditional models often rely on historical data and human assumptions, which may miss evolving threats. AI, on the other hand, adapts to changing data patterns, learns from new inputs, and predicts emerging risks with high precision—offering FinTech firms a proactive edge.
3. Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency
By automating labor-intensive tasks like regulatory checks, customer verification, and reporting, AI reduces the burden on risk teams and cuts down operational costs. This allows human resources to focus on more strategic tasks while ensuring round-the-clock risk monitoring.
4. Enhanced Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
AI tools can scan legal databases and flag updates in regulatory frameworks, ensuring that compliance procedures remain current. They also generate audit-ready documentation, simplifying regulatory reporting and reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
5. Scalability and Adaptability
As FinTech companies grow and onboard more users, AI systems scale effortlessly to handle higher volumes of transactions and data without compromising performance. This makes AI a sustainable solution for both startups and large enterprises.
Drawbacks Using AI in FinTech Risk Management
1. Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI models are only as good as the data they’re trained on. If the training data contains historical biases or lacks diversity, the AI may unfairly target certain groups, especially in areas like credit risk scoring or fraud detection—leading to regulatory and reputational risks.
2. Lack of Transparency (Black Box Problem)
Many AI models, especially deep learning systems, function like a “black box,” offering little insight into how decisions are made. This opacity can be a major hurdle when regulators require clear justifications for risk assessments and actions.
3. High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
Developing and deploying AI systems involves significant upfront investment in data infrastructure, talent, and training. Ongoing maintenance, updates, and model retraining also add to the long-term costs, which can be a barrier for smaller FinTech firms.
4. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
AI relies on massive datasets, including sensitive financial and personal information. If not managed properly, this can increase the risk of data leaks, breaches, or misuse—raising concerns about user trust and legal compliance with data protection laws.
5. Over-Reliance and Reduced Human Oversight
While automation is beneficial, over-dependence on AI may lead to complacency. Certain complex or nuanced decisions still require human judgment. A system that operates entirely on autopilot might overlook red flags that don’t fit predefined patterns.
Developing a FinTech Risk Management Framework
Creating a solid risk management framework is essential for any FinTech company aiming to operate safely, scale efficiently, and maintain customer trust. Unlike traditional financial institutions, FinTechs often face a unique blend of digital, operational, and regulatory risks. A well-developed framework serves as a blueprint for identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring those risks. It aligns teams, technologies, and policies around a shared risk strategy—allowing the company to respond quickly and effectively when issues arise. This proactive approach not only minimizes financial losses but also supports long-term growth and regulatory compliance.
Here are the key steps to developing a FinTech risk management framework:
1. Appoint Internal Risk Leaders and Define Roles: Assign dedicated risk managers or teams to oversee risk strategy, governance, and response plans. Clear role definitions help prevent gaps in responsibility.
2. Identify and Categorize All Relevant Risks: Map out the different types of risks the organization faces—such as financial, cybersecurity, regulatory, operational, and reputational—and assess their potential impact and likelihood.
3. Evaluate Internal Processes and Resources: Review existing systems, processes, and tools to identify vulnerabilities and assess how well current resources can handle emerging threats.
4. Monitor Market Trends and External Threats: Stay informed on evolving industry threats, regulatory changes, and new technologies that could affect risk exposure. This includes tracking competitors and geopolitical developments.
5. Conduct Risk Assessments and Scenario Planning: Perform regular risk assessments, including stress tests and simulations, to evaluate how the business would respond to worst-case scenarios.
6. Define Mitigation and Response Strategies: Develop clear action plans for each risk category, including how to avoid, reduce, transfer, or retain risks. These strategies should be regularly updated based on performance and new threats.
7. Establish Internal Communication and Reporting Protocols: Create structured reporting channels to ensure risk-related information flows quickly to decision-makers. Dashboards and automated alerts can support real-time monitoring.
8. Integrate Technology and Automation: Use risk management software, AI, and analytics tools to streamline compliance, detect threats early, and reduce manual errors.
9. Build a Risk-Aware Culture: Educate employees across departments on the importance of risk awareness, compliance, and cybersecurity best practices through ongoing training and clear policies.
10. Review and Improve the Framework Regularly: The risk landscape is always evolving. Regular audits, feedback loops, and performance reviews are essential for refining the framework and ensuring its long-term effectiveness.
Best Practices for Implementing Risk Management Software
Implementing risk management software is a critical step for FinTech companies looking to strengthen their defenses against financial, operational, and regulatory threats. However, simply adopting the software isn’t enough—it must be integrated thoughtfully and strategically to deliver real value. A successful implementation requires clear planning, cross-functional collaboration, and continuous improvement. By following best practices, companies can ensure the software becomes an effective tool that enhances decision-making, reduces risk exposure, and supports business growth.
Here are the best practices for implementing risk management software in a FinTech environment:
1. Define Clear Objectives and Risk Priorities: Before implementation, outline what the software should achieve—whether it’s reducing fraud, improving compliance, or enhancing data visibility. Align the goals with the company’s specific risk profile.
2. Involve Cross-Functional Teams Early: Risk management touches multiple departments including compliance, IT, operations, and finance. Involving stakeholders from each area ensures the system is designed to meet everyone’s needs and encourages buy-in.
3. Choose Software with Scalable Integration Capabilities: Select a solution that can integrate easily with existing platforms such as CRMs, payment gateways, and analytics tools, ensuring a unified view of risk across the business.
4. Customize the System to Fit Your Operations: Configure workflows, dashboards, and alerts based on your organization’s unique processes and risk categories. Avoid one-size-fits-all setups that may not address your key vulnerabilities.
5. Automate Where Possible, But Maintain Human Oversight: Use automation for tasks like transaction monitoring, compliance checks, and reporting—but ensure critical decisions still involve human review to catch context-based issues.
6. Train Staff Thoroughly: Provide comprehensive training for users across all relevant departments to ensure proper usage, faster adoption, and fewer errors during operation.
7. Establish Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation: Track performance metrics and risk indicators post-implementation to assess effectiveness. Use insights from the software to refine policies and response strategies continuously.
8. Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes: Ensure the software is regularly updated to accommodate new regulatory requirements. Some platforms offer automated updates that keep compliance features current.
9. Test the System with Real-World Scenarios: Run simulations and mock threat scenarios to validate how the software performs under pressure and refine response protocols accordingly.
10. Create Feedback Loops for Continuous Improvement: Encourage feedback from users and stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. Use this input to fine-tune the system and adapt to changing risk landscapes.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving FinTech landscape, where innovation meets complexity, effective risk management is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. Risk management software plays a vital role in helping companies navigate regulatory demands, protect against fraud, and minimize financial losses through real-time monitoring, automation, and predictive analytics. When combined with AI and supported by a clear risk framework, this technology empowers FinTech firms to operate with greater agility, security, and confidence. By understanding the types of risks, implementing strategic controls, and leveraging the right tools, FinTech companies can build resilient operations that not only survive challenges but thrive in a highly competitive market.



