In today’s digital age, fake news has become a pervasive and complex issue, undermining trust in institutions, distorting public perception, and fueling societal divides. The ease of sharing information on social media, coupled with advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, has blurred the line between fact and fiction, making it harder than ever to discern credible news from misinformation. However, blockchain technology offers a promising solution. By leveraging its core features—decentralization, transparency, and immutability—blockchain can revolutionize how we verify, authenticate, and distribute information, creating a robust defense against the spread of fake news. This article explores how blockchain technology can combat misinformation and restore integrity to the information ecosystem.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger designed to securely record transactions and information across a network of computers. Each entry, or “block,” is linked to the previous one through cryptographic techniques, forming a secure and immutable chain of data. Unlike traditional databases controlled by a single entity, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, ensuring that no single party can alter the recorded information. Initially developed to support cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain has evolved to offer solutions far beyond finance, including enhancing data security, transparency, and trust in various industries. Its unique ability to provide a tamper-proof record makes it particularly valuable in combating challenges like misinformation and fake news.
What is Fake News?
Fake news refers to false or misleading information presented as legitimate news with the intent to deceive, manipulate, or provoke a reaction. It often takes various forms, such as fabricated stories, manipulated visuals, or misrepresented facts, and is designed to exploit biases, emotions, or misinformation gaps in its audience. Fake news can range from satire or parody that is misinterpreted as truth to deliberately false content created to serve political, financial, or social agendas. Its impact is far-reaching, influencing public opinion, damaging reputations, and undermining trust in credible institutions. With the rise of social media and digital platforms, fake news spreads rapidly, making it a critical issue in today’s information-driven world.
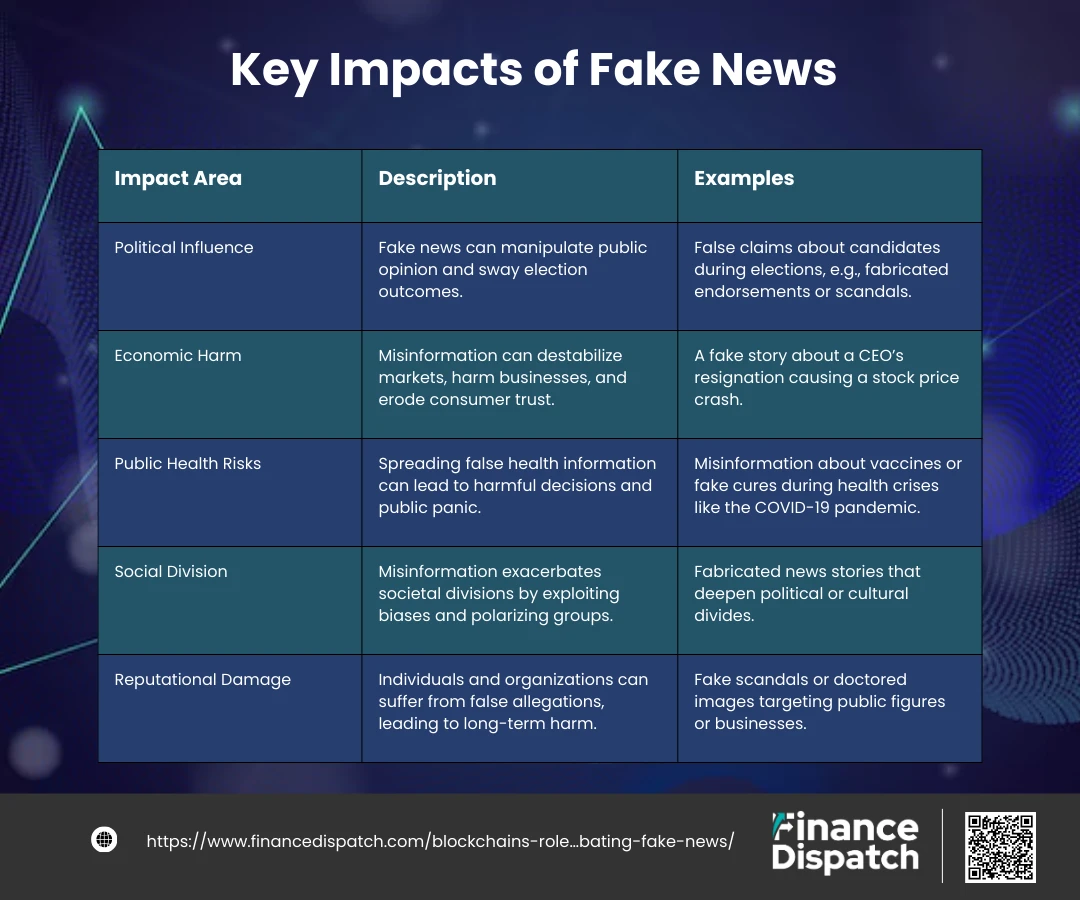
Key Impacts of Fake News
| Impact Area | Description | Examples |
| Political Influence | Fake news can manipulate public opinion and sway election outcomes. | False claims about candidates during elections, e.g., fabricated endorsements or scandals. |
| Economic Harm | Misinformation can destabilize markets, harm businesses, and erode consumer trust. | A fake story about a CEO’s resignation causing a stock price crash. |
| Public Health Risks | Spreading false health information can lead to harmful decisions and public panic. | Misinformation about vaccines or fake cures during health crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Social Division | Misinformation exacerbates societal divisions by exploiting biases and polarizing groups. | Fabricated news stories that deepen political or cultural divides. |
| Reputational Damage | Individuals and organizations can suffer from false allegations, leading to long-term harm. | Fake scandals or doctored images targeting public figures or businesses. |
How Blockchain Can Solve the Problem of Fake News
Blockchain technology offers innovative solutions to address the challenges posed by fake news. By leveraging its core principles—decentralization, transparency, and immutability—blockchain can verify the authenticity of information, trace its origin, and foster accountability. This not only limits the spread of misinformation but also restores trust in the news ecosystem.
1. Immutable Records of Content
Blockchain creates an unchangeable record of all information stored on its ledger. Once a news article or piece of content is uploaded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the preservation of the original content, allowing users to verify its authenticity at any time. Even if an individual or entity tries to manipulate or discredit the content, the blockchain ensures the original remains intact and accessible.
2. Decentralized Verification
Unlike traditional verification processes controlled by a central authority, blockchain relies on a network of distributed nodes to validate information. Each node independently verifies the content, ensuring that the process is unbiased and free from manipulation. This decentralized approach eliminates single points of failure, making it significantly harder for fake news to infiltrate the system.
3. Source Authentication
Blockchain allows content creators to attach digital signatures to their work using cryptographic tools. These signatures confirm the creator’s identity and verify the authenticity of the content. For example, journalists or media organizations can use blockchain to prove the legitimacy of their reports, ensuring consumers that the news originates from credible sources.
4. Transparent Content Provenance
Every piece of content on the blockchain is accompanied by metadata that records its origin, timestamp, and subsequent modifications. This transparency enables users to trace the history of a news story, verify its original source, and review any changes made over time. Such traceability fosters trust and accountability in the news ecosystem.
5. Automated Fact-Checking with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts—self-executing programs on the blockchain—can streamline the verification process. For instance, they can automatically cross-reference news articles with trusted databases or fact-checking organizations to validate their accuracy. This automation reduces the time required for manual checks, ensuring misinformation is flagged before it spreads.
6. Crowdsourced Verification Systems
Blockchain platforms can empower communities to collaboratively verify news content. Users can rate, flag, or validate articles, leveraging the collective intelligence of a diverse audience. This “wisdom of the crowd” approach democratizes the fact-checking process, ensuring multiple perspectives contribute to identifying fake news.
7. Tokenized Incentives for Fact-Checkers
Blockchain platforms can introduce token-based systems to reward users who participate in verifying content or flagging misinformation. For example, users might earn tokens for successfully identifying fake news, which they can exchange for goods, services, or monetary value. This incentivized model encourages active participation, fostering a robust fact-checking community.
8. Combatting Deepfakes and Digital Manipulations
Blockchain can store metadata of original images, videos, and audio files, providing a verifiable record of their authenticity. By comparing metadata, users can detect whether content has been manipulated, ensuring that deepfakes or altered media do not gain credibility. This technology protects the integrity of digital content and helps prevent the spread of fake visuals or audio.
9. Reduced Censorship Risks
The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it resistant to censorship and external interference. Governments, corporations, or other entities cannot easily suppress or manipulate verified information stored on the blockchain. This ensures that credible news remains accessible, even in environments where freedom of speech and press are restricted.
10. Global Standardization of News Credibility
Blockchain can facilitate the establishment of universal standards for evaluating the credibility of news sources. By using blockchain to record and verify information according to global protocols, media platforms can adopt consistent methods for authenticating content. This standardization promotes trust and reliability across international news ecosystems.

Use Cases and Examples
Blockchain technology is already making strides in combating fake news through various innovative applications. By ensuring transparency, authenticity, and accountability, these real-world use cases showcase how blockchain can reshape the media landscape and fight misinformation effectively.
1. The News Provenance Project
Launched by The New York Times, this initiative focuses on combating misinformation in visual content. By leveraging blockchain, the project attaches metadata, including timestamps and editing history, to images and videos. Users can access this information to verify the authenticity of the content and identify whether it has been manipulated or taken out of context. This application highlights blockchain’s potential to bring transparency to digital media, safeguarding its integrity.
2. Po.et: Tracking Intellectual Property Rights
Po.et is a blockchain-based platform designed to track and manage intellectual property rights for digital content. By timestamping and recording the creation details of articles, images, or videos on the blockchain, content creators can prove ownership and authenticity. This reduces the risk of content theft, plagiarism, or misrepresentation, while also ensuring that fake or unauthorized versions of the content cannot be circulated.
3. Deep Trust Alliance
The Deep Trust Alliance is a global coalition dedicated to tackling deepfakes and misinformation. Using blockchain technology, the alliance records licensing details and metadata for digital media. This system enables automated verification of content authenticity, making it easier to detect and flag fake or unauthorized media, thereby upholding media integrity.
4. Userfeeds: Ranking Content by Credibility
Userfeeds uses blockchain to create a ranking system for online content, prioritizing credibility and trustworthiness. The platform incentivizes users with tokens to verify and flag fake news, fostering a collaborative environment for content validation. By linking rankings to blockchain’s immutable records, Userfeeds ensures transparency in the credibility assessment of news articles.
5. PUBLIQ: Decentralized Journalism Platform
PUBLIQ is a blockchain-based platform promoting accurate and reliable journalism. It rewards authors based on their PUBLIQ score, which reflects their reputation and the quality of their content. The decentralized structure ensures freedom from censorship, while the reward system discourages the spread of fake news by incentivizing factual reporting.
6. Fact Protocol: Decentralized Fact-Checking System
Fact Protocol employs a two-layer verification process to validate news. The first layer involves fact-checkers (news registrars) who verify claims in an article. The second layer consists of validators who cross-check the fact-checkers’ work to ensure accuracy. This decentralized approach, powered by blockchain, minimizes bias and ensures thorough verification, making it a robust tool against misinformation.
7. AMP: Blockchain for Media Accountability
Associated Press (AP) utilizes blockchain to track the ownership and authenticity of its media content. This prevents unauthorized use and ensures that journalists and media outlets are credited for their work. It also guarantees that the content consumed by the public remains unaltered, helping maintain trust in news media.
8. Blockchain in Political Campaigns
Blockchain has been used to maintain transparent records of political campaign finances, advertisements, and other key activities. By recording these details on an immutable ledger, blockchain ensures accountability and prevents the spread of fake narratives regarding campaign activities or funding sources. This fosters transparency in democratic processes.
9. Verified Health News During COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, blockchain-based platforms played a critical role in combating health-related misinformation. They ensured that only verified sources contributed information about treatments, vaccines, and safety guidelines. By creating a transparent and traceable system for health news, blockchain helped reduce public confusion and build trust in credible health information.
10. Educational Initiatives Using Blockchain
Blockchain is being integrated into educational programs to promote media literacy and critical thinking. These platforms use blockchain to demonstrate how content can be verified for authenticity, teaching users to identify misinformation. By empowering individuals to discern fake news from credible reports, such initiatives help cultivate a more informed and skeptical audience.

Challenges and Limitations Blockchain fake news verification
While blockchain technology offers promising solutions to tackle fake news and enhance media integrity, its implementation is not without challenges. Issues such as scalability, accessibility, and regulatory hurdles must be addressed for blockchain to become a mainstream tool in the fight against misinformation.
1. Scalability Issues
Blockchain networks often face challenges when handling large volumes of data and transactions. As news platforms grow to serve global audiences and manage extensive content, the need for high transaction speeds and large-scale data storage increases. Blockchain’s existing scalability limitations, such as slow processing times and data bloat, could impede its ability to operate efficiently on a large scale, especially for platforms that require real-time news verification.
2. High Costs
Setting up and maintaining a blockchain system can be prohibitively expensive. The costs associated with infrastructure development, skilled personnel, and ongoing operations can make blockchain adoption difficult for smaller media organizations or independent journalists. Additionally, transaction fees on public blockchains, which fluctuate based on network demand, can create financial uncertainty for users.
3. Complexity and Accessibility
Blockchain’s technical nature can make it intimidating for non-technical users, such as journalists, editors, and the general public. Adopting blockchain-based systems may require significant training or hiring technical experts, which could slow down adoption. Furthermore, user interfaces for blockchain platforms may not yet be intuitive enough for widespread use, creating a barrier for entry.
4. Energy Consumption
Many blockchain systems, particularly those using Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanisms, consume large amounts of energy for mining and validating transactions. This high energy demand raises environmental concerns, especially when deploying blockchain solutions at scale. Moving to energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake (PoS) can mitigate this, but not all platforms have transitioned to these alternatives.
5. Regulatory Uncertainty
Blockchain operates in a regulatory gray area in many regions, with laws struggling to keep up with the technology’s rapid evolution. Issues such as data immutability may conflict with privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which requires the ability to delete personal data. This legal uncertainty can deter media organizations from adopting blockchain for news verification.
6. Potential for Misuse
Blockchain’s transparent and immutable nature can be exploited by malicious actors. For instance, while the technology ensures that data cannot be altered, bad actors could intentionally input misleading or biased information that appears credible because it is recorded on the blockchain. This could create a false sense of trust among users.
7. Integration with Existing Systems
Legacy systems used by traditional media outlets may not easily integrate with blockchain’s decentralized architecture. Transitioning to blockchain requires significant infrastructure upgrades and changes in workflow, which can be disruptive and costly. Ensuring compatibility with current systems is a complex challenge that requires careful planning and resources.
8. Trust in Initial Data Entry
Blockchain ensures data integrity after it is recorded, but it cannot verify the authenticity of information at the point of entry. If fake or manipulated data is added to the blockchain, it becomes part of the permanent record. This limitation highlights the need for robust mechanisms to validate content before it is entered into the blockchain system.
9. Limited Public Awareness
Many people are unfamiliar with blockchain technology and its applications in combating fake news. This lack of awareness can create mistrust or reluctance to adopt blockchain-enabled platforms. Without effective education and outreach, blockchain may fail to gain the widespread acceptance needed for significant impact.
10. Lack of Standardization
The absence of global standards for implementing blockchain in media creates inconsistencies in how the technology is applied. Different platforms may use varying approaches, making it difficult to establish unified verification protocols or share data across systems. This fragmentation could hinder collaboration and slow the technology’s adoption in the fight against fake news.
The Future of Blockchain in Combating Fake News
The future of blockchain in combating fake news lies in its ability to integrate seamlessly with emerging technologies and media ecosystems, creating a robust and trustworthy framework for information dissemination. As blockchain evolves, it is expected to combine with artificial intelligence for automated fact-checking, enabling real-time verification of news content. Decentralized platforms may become more widespread, empowering communities to collectively validate information while reducing reliance on centralized authorities prone to bias or manipulation. Advances in energy-efficient consensus mechanisms and regulatory clarity will further drive blockchain’s adoption, addressing scalability, cost, and legal concerns. With continued innovation and collaboration, blockchain has the potential to transform the media landscape, ensuring the authenticity of information and restoring public trust in news.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to tackling the pervasive problem of fake news, addressing key challenges with its features of transparency, decentralization, and immutability. By enabling verified content, fostering trust, and empowering community-driven fact-checking, blockchain can reshape the media landscape and restore integrity to information dissemination. While challenges like scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and accessibility remain, ongoing innovation and collaboration can overcome these hurdles. The integration of blockchain with emerging technologies and the development of global standards hold immense promise for creating a future where misinformation is minimized, and credible information thrives. As blockchain continues to evolve, it has the potential to become a cornerstone in the fight against fake news, safeguarding the truth and rebuilding trust in the digital age.
FAQs
1. Can blockchain eliminate fake news entirely?
Blockchain can significantly reduce the spread of fake news by verifying content authenticity and ensuring transparency, but it cannot eliminate misinformation completely. Factors such as human error, intentional manipulation during data entry, and lack of public awareness about blockchain’s role can still allow fake news to persist.
2. How does blockchain handle opinion-based or editorial content?
Blockchain is best suited for verifying factual information and source authenticity. For opinion-based or editorial content, it can provide transparency about the author and publication history, but it cannot judge the validity of subjective viewpoints or opinions.
3. What role can blockchain play in social media platforms to combat fake news?
Blockchain can be integrated into social media platforms to create decentralized verification systems. Users could flag misinformation, and blockchain’s immutable ledger could track the origin and dissemination of posts, ensuring accountability for shared content.
4. How can blockchain address misinformation spread through AI-generated content, such as deepfakes?
Blockchain can store metadata of original content, making it easier to identify manipulated versions. Additionally, combining blockchain with AI tools can help detect and flag deepfake content, providing a mechanism to verify the authenticity of media.
5. What steps can governments take to promote the use of blockchain against fake news?
Governments can support blockchain adoption by funding pilot projects, creating regulatory frameworks to encourage innovation, and collaborating with technology companies to develop standardized systems for news verification. Public education campaigns to raise awareness of blockchain’s benefits in combating misinformation can also drive adoption.




