Cryptocurrencies have revolutionized the way we think about money, offering a decentralized and digital alternative to traditional currencies. While they have gained widespread acceptance and adoption in many parts of the world, not every country shares the enthusiasm. Several nations have imposed outright bans or severe restrictions on cryptocurrencies, citing concerns over financial stability, consumer protection, and the potential for illegal activities. This article explores the countries where cryptocurrency is banned, delving into the reasons behind these prohibitions and how they impact the global crypto landscape.
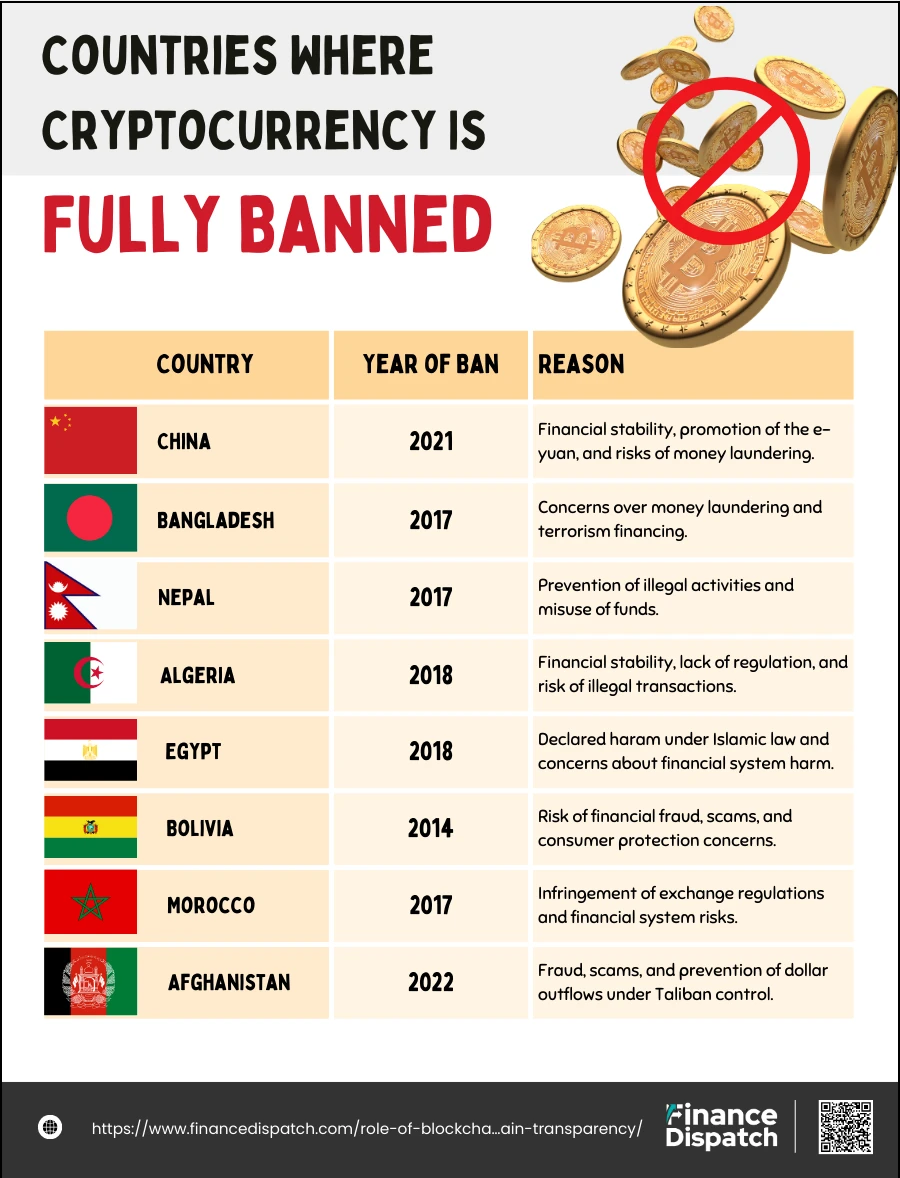
Countries Where Cryptocurrency Is Fully Banned
Some countries have taken a firm stance against cryptocurrencies, completely banning their use, trading, mining, or possession. These bans often stem from concerns about financial stability, consumer protection, and the potential misuse of cryptocurrencies for illegal activities. Below is a table highlighting countries where cryptocurrency is fully banned and the year of implementation:
| Country | Year of Ban | Reason for Ban |
| China | 2021 | Financial stability, promotion of the e-yuan, and risks of money laundering. |
| Bangladesh | 2017 | Concerns over money laundering and terrorism financing. |
| Nepal | 2017 | Prevention of illegal activities and misuse of funds. |
| Algeria | 2018 | Financial stability, lack of regulation, and risk of illegal transactions. |
| Egypt | 2018 | Declared haram under Islamic law and concerns about financial system harm. |
| Bolivia | 2014 | Risk of financial fraud, scams, and consumer protection concerns. |
| Morocco | 2017 | Infringement of exchange regulations and financial system risks. |
| Afghanistan | 2022 | Fraud, scams, and prevention of dollar outflows under Taliban control. |
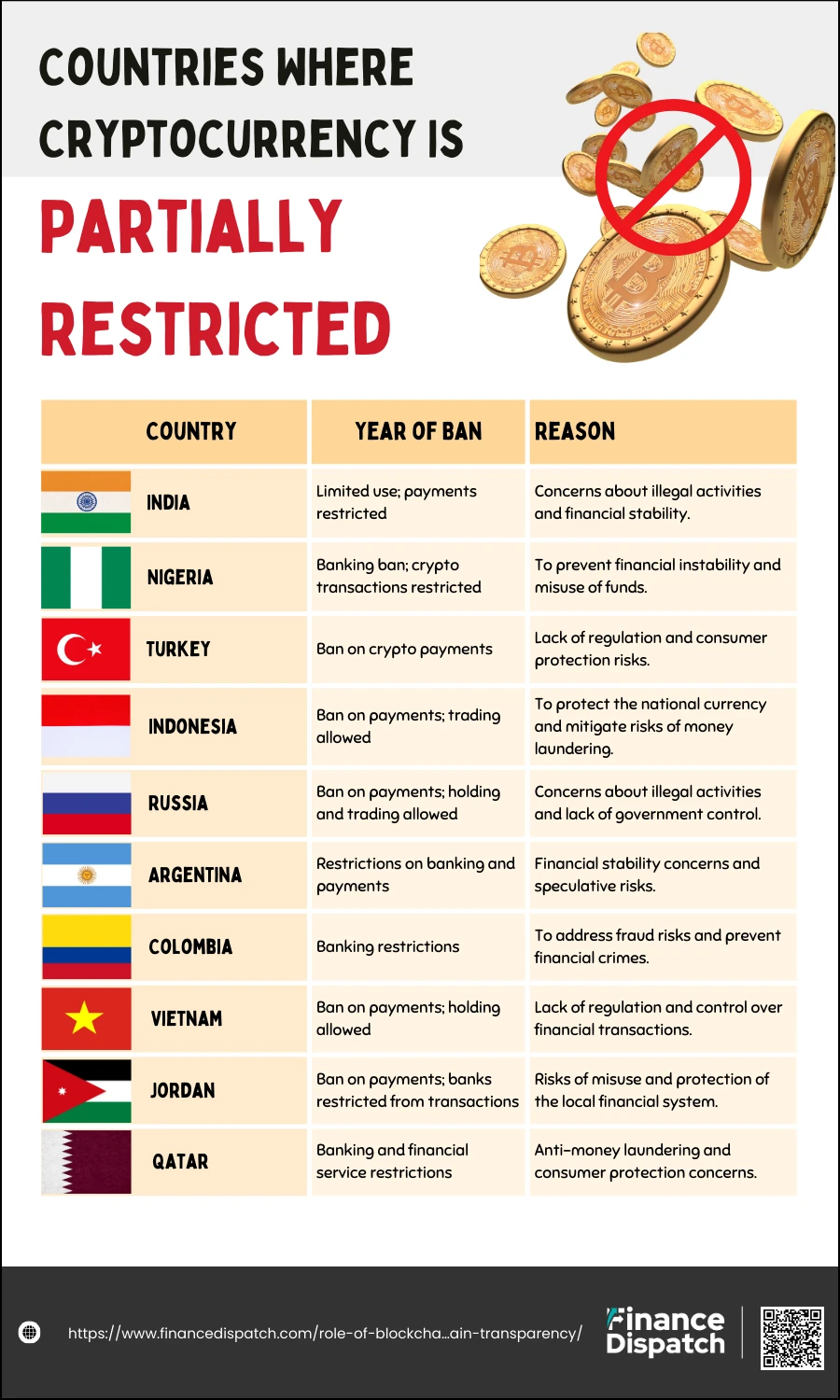
Countries Where Cryptocurrency Is Partially Restricted
While some countries have outright banned cryptocurrencies, others have imposed partial restrictions, allowing certain activities while prohibiting others. These restrictions often target cryptocurrency payments, mining, or banking services to address concerns about financial stability, illegal activities, and consumer protection. Below is a table summarizing countries with partial restrictions on cryptocurrency:
| Country | Type of Restriction | Reason for Restriction |
| India | Limited use; payments restricted | Concerns about illegal activities and financial stability. |
| Nigeria | Banking ban; crypto transactions restricted | To prevent financial instability and misuse of funds. |
| Turkey | Ban on crypto payments | Lack of regulation and consumer protection risks. |
| Indonesia | Ban on payments; trading allowed | To protect the national currency and mitigate risks of money laundering. |
| Russia | Ban on payments; holding and trading allowed | Concerns about illegal activities and lack of government control. |
| Argentina | Restrictions on banking and payments | Financial stability concerns and speculative risks. |
| Colombia | Banking restrictions | To address fraud risks and prevent financial crimes. |
| Vietnam | Ban on payments; holding allowed | Lack of regulation and control over financial transactions. |
| Jordan | Ban on payments; banks restricted from transactions | Risks of misuse and protection of the local financial system. |
| Qatar | Banking and financial service restrictions | Anti-money laundering and consumer protection concerns. |
Countries Where Crypto is a Legal Tender
Only a few countries have gone as far as declaring cryptocurrency a legal tender, allowing it to be used alongside their national currencies for transactions. These countries have embraced the innovation of cryptocurrencies, aiming to boost financial inclusion, attract foreign investments, or drive economic growth. Here are the countries where crypto holds the status of legal tender:
1. El Salvador
In 2021, El Salvador became the first country in the world to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender. President Nayib Bukele introduced the initiative to promote financial inclusion and reduce reliance on remittances through traditional banking. Businesses in El Salvador are now required to accept Bitcoin alongside the U.S. dollar, which remains the country’s primary fiat currency. The government also created the Chivo Wallet app to facilitate transactions and established a Bitcoin trust to stabilize conversion rates.
2. Central African Republic (CAR)
The Central African Republic followed El Salvador in 2022, becoming the second country to declare Bitcoin as legal tender. The move was intended to modernize the nation’s financial system and attract investment in a country with limited banking infrastructure. However, adoption has been slow due to low internet penetration and limited understanding of cryptocurrency among the population. Despite these challenges, the CAR government continues to explore blockchain technology for economic development.
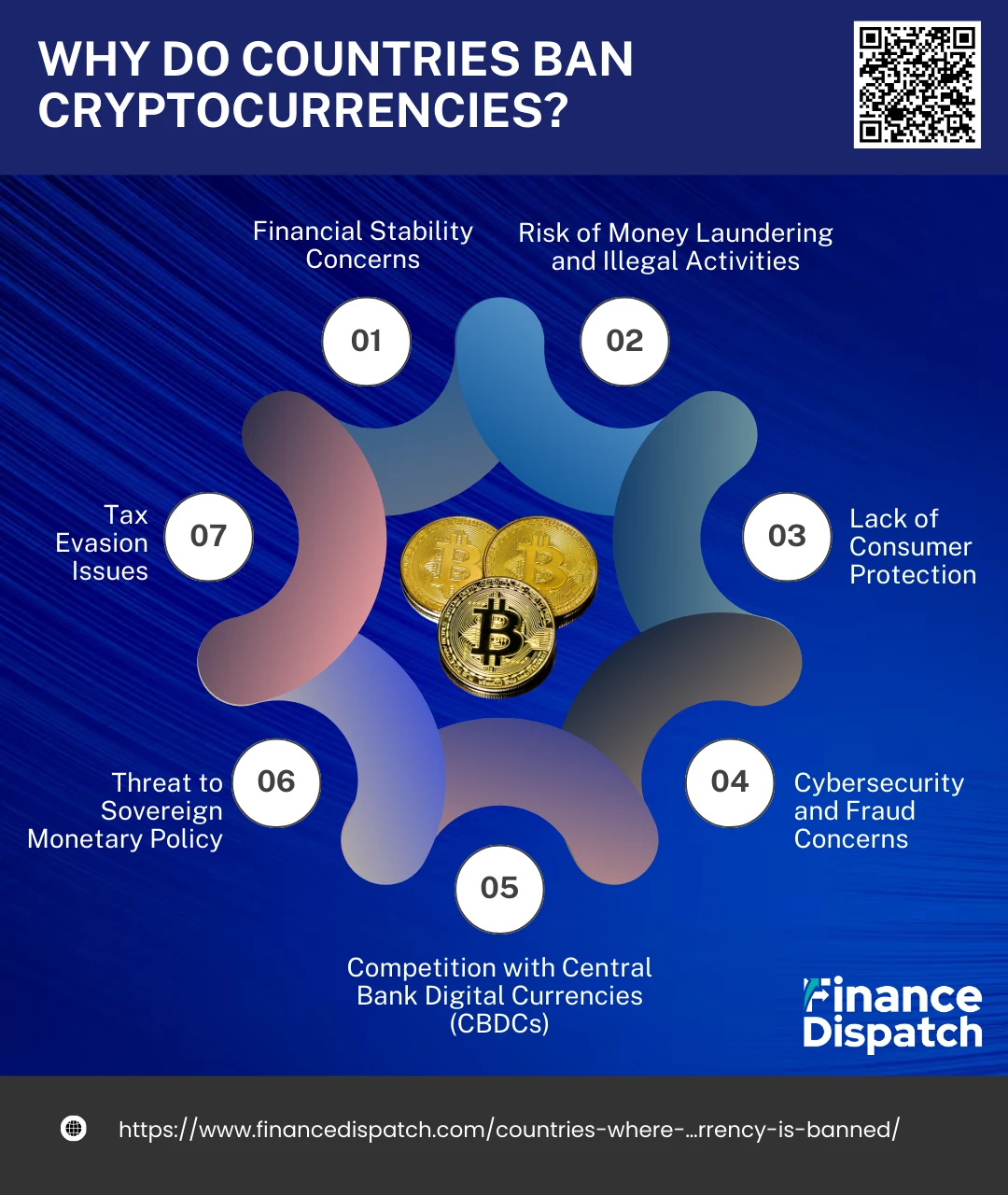
Why Do Countries Ban Cryptocurrencies?
Some countries choose to ban cryptocurrencies due to the challenges and risks they present to financial systems, consumer protection, and national security. While cryptocurrencies promise decentralization and innovation, their unregulated nature and potential misuse have made several governments wary. Here are the primary reasons behind these bans:
1. Financial Stability Concerns
Cryptocurrencies are notoriously volatile, with values that can fluctuate dramatically in short periods. This instability poses a threat to domestic economies, especially in countries with less robust financial systems. Governments fear that widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies could undermine their ability to manage monetary policy, control inflation, or stabilize their national currencies. In extreme cases, a sudden crypto market crash could lead to significant financial losses for investors and ripple effects across the economy.
2. Risk of Money Laundering and Illegal Activities
One of the most debated aspects of cryptocurrencies is their potential to facilitate illegal activities. Due to their pseudonymous nature, cryptocurrencies make it difficult to trace transactions, creating opportunities for money laundering, terrorism financing, and other illicit activities. Criminal networks have been known to exploit these digital assets for transferring funds without detection, prompting governments to enforce strict regulations or outright bans to curb such risks.
3. Lack of Consumer Protection
Unlike traditional banking and investment systems, cryptocurrency markets often lack regulatory oversight and fail to offer mechanisms for consumer protection. Investors face the risk of falling victim to Ponzi schemes, fraudulent Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), and manipulative trading practices. Without proper safeguards, consumers are also vulnerable to losing their investments due to cyberattacks or the collapse of exchanges, further fueling governments’ concerns.
4. Tax Evasion Issues
Cryptocurrency transactions are notoriously difficult to track, which can make it easier for individuals and businesses to evade taxes. As these digital assets operate outside the traditional financial system, governments face significant challenges in enforcing tax compliance. This evasion could lead to substantial revenue losses, prompting authorities to ban or restrict crypto activities to maintain fiscal order.
5. Threat to Sovereign Monetary Policy
Governments and central banks use monetary policy as a tool to regulate economic growth and control inflation. Cryptocurrencies, being decentralized and not tied to any central authority, present a challenge to this control. Their widespread use could weaken governments’ ability to enforce monetary policies, issue currency, and regulate financial activities, thereby undermining their sovereignty.
6. Competition with Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Many countries are developing their own Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) to leverage the benefits of blockchain technology while maintaining control over their financial systems. Private cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, are viewed as competition that could reduce the adoption of CBDCs. To ensure their digital currencies gain traction, some governments have opted to ban or restrict private cryptocurrencies.
7. Cybersecurity and Fraud Concerns
The cryptocurrency space has been plagued by high-profile hacks, scams, and frauds, with billions of dollars stolen annually. These incidents not only erode public trust but also expose users to significant financial risks. Governments fear that the prevalence of cybercrime in the crypto industry could destabilize their financial systems and lead to public discontent. By banning cryptocurrencies, authorities aim to protect their citizens from falling victim to these threats.
Future of Cryptocurrency in Banned Countries
The future of cryptocurrency in banned countries remains uncertain yet promising, as evolving technologies and global trends challenge the longevity of strict prohibitions. While governments in these nations cite financial stability, consumer protection, and national security as reasons for bans, the growing global acceptance of cryptocurrencies and blockchain innovation could push these countries to reconsider their stance. For example, the rise of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) may create a bridge between decentralized cryptocurrencies and government-regulated digital systems, potentially easing restrictions over time. Additionally, increasing demand for financial inclusion and global investment opportunities might prompt banned countries to explore more balanced regulatory frameworks. As blockchain technology continues to mature, these nations could pivot toward controlled adoption, leveraging crypto’s potential for economic growth while maintaining oversight.
Conclusion
The global stance on cryptocurrency reflects a complex interplay of innovation, regulation, and risk management. While some countries have embraced cryptocurrencies as tools for financial inclusion and economic growth, others have implemented bans to safeguard financial stability, prevent illicit activities, and maintain control over monetary policy. Despite these restrictions, the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies often enables their continued use, challenging enforcement and shaping underground markets. As blockchain technology evolves and global acceptance of digital assets grows, even banned countries may reconsider their approaches, exploring controlled adoption or integrating cryptocurrencies into their financial systems. Ultimately, the future of cryptocurrency lies in striking a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring stability and security, offering endless possibilities for economies worldwide.
FAQs
1. How do cryptocurrency bans impact international trade and remittances?
Cryptocurrency bans can disrupt international trade and remittances, especially in countries heavily reliant on cross-border transactions. Digital currencies often provide faster and cheaper transfer methods compared to traditional banking systems. Restrictions limit these benefits, pushing users toward less efficient or informal alternatives.
2. Can citizens in banned countries still access cryptocurrency markets?
Yes, despite bans, many individuals in restricted countries use VPNs, decentralized exchanges, or peer-to-peer platforms to access cryptocurrency markets. However, such activities often operate in legal gray areas, exposing users to risks like fraud and lack of consumer protection.
3. What role do global financial organizations play in influencing crypto regulations in banned countries?
International bodies like the IMF or FATF play a significant role by setting global standards for anti-money laundering (AML) and financial stability, which influence crypto policies. These guidelines often push countries toward stricter regulations or outright bans if compliance appears challenging.
4. Are there any global trends indicating a reversal of crypto bans?
Yes, some countries with strict bans are reconsidering their stance as blockchain technology gains mainstream acceptance. For instance, nations developing Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) may eventually ease restrictions on private cryptocurrencies to complement their digital ecosystems.
5. How does the lack of crypto regulations in banned countries affect technological innovation?
Strict bans can stifle local blockchain innovation, forcing developers and startups to relocate to more crypto-friendly jurisdictions. This “brain drain” not only impacts technological progress within the country but also limits its ability to participate in the global digital economy.